Scientific Analysis of Boldenone Counterfeiting: How ATD Became the Main Deception on the Black Market
As you know, I've been working as an online trainer for more than 10 years, and lately I've been increasingly encountering the same problem: guys who buy pharma independently complain about strange symptoms, and their tests after a cycle of so-called "boldenone" show a sharp drop in estradiol levels, down to zero values.
The situation is aggravated by the fact that sellers from dubious shops actively convince buyers that boldenone is supposed to lower estradiol. However, having medical education, I understand that this is biochemically impossible—real Bold cannot produce such an effect. It became obvious that we're dealing with large-scale counterfeiting.
The problem is that under the guise of good old Boldenone, illegal manufacturers sell 1,4,6-androstatriene-3,17-dione—a substance known as ATD. This substitution is not just replacing one steroid with another, but fundamental deception, since ATD and boldenone are compounds with radically different effects on the body.
This problem has already become personal for me, as it constantly confuses my cycle control cards, while people themselves remain puzzled about why this happens. Therefore, I decided to conduct my own investigation to establish the real composition of these drugs and explain how they actually affect the body.
- Boldenone is valued by users for its anabolic properties that promote muscle mass growth.
- ATD is a powerful aromatase inhibitor whose main purpose is not muscle growth, but radical reduction of estrogen levels in the body.
The key feature of this deception, which makes it so convincing, lies in metabolism. It's scientifically proven that ATD in the human body converts (metabolizes) into Boldenone. Thus, the consumer using the counterfeit faces a double effect:
- They experience powerful anti-estrogenic action from ATD, which leads to estradiol drop and accompanying side effects (joint pain, libido drop).
- At the same time, some amount of Boldenone is actually formed in their body, which can be confirmed by laboratory analysis, creating a false sense of confidence in the drug's authenticity in the user.
This scheme is aggravated by the historical availability of ATD. For a long time it was part of over-the-counter sports supplements, which allowed accumulating both significant raw material reserves and knowledge about its synthesis methods. After bans, these resources were easily redirected to black market needs, creating a stable base for counterfeit production.
Now we'll analyze this problem in detail, I'll explain the biochemical mechanisms underlying it, and provide scientific data for reasoned dialogue with "reliable sellers from whom everyone buys and everyone likes everything."
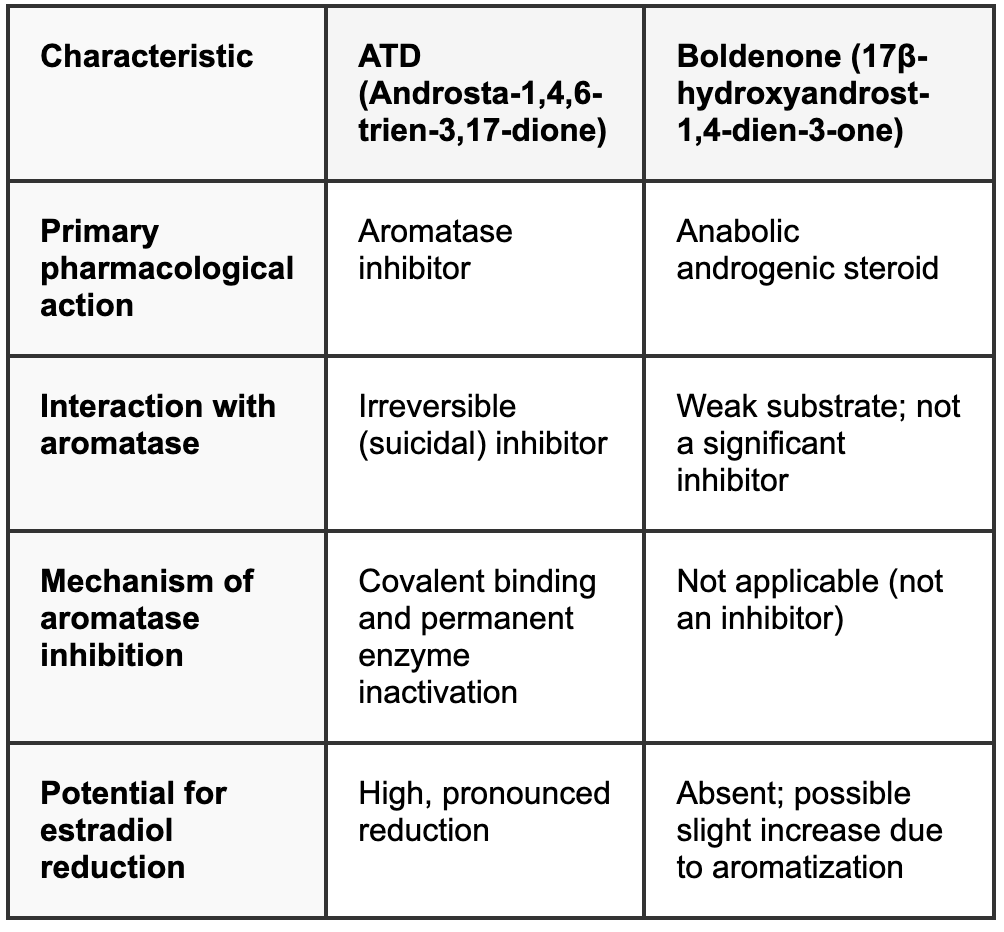
Two different substances: Comparative analysis of ATD and Boldenone
To understand the essence of the deception, it's necessary to clearly distinguish the biochemical profiles of these two compounds.
ATD (Androsta-1,4,6-triene-3,17-dione): Powerful estrogen suppressor
ATD is a steroid compound whose unique structure with three double bonds in the molecule determines its specific activity. It's classified as a powerful irreversible (suicide) aromatase inhibitor.
Aromatase is an enzyme responsible for a key stage in estrogen biosynthesis: converting androgens (e.g., testosterone) into estrogens (e.g., estradiol). ATD's mechanism of action consists of firmly binding with this enzyme and irreversibly deactivating it, forming a covalent bond. Such inactivation means that to restore normal estrogen synthesis levels, the body needs to produce completely new aromatase enzyme molecules, which requires significant time. This precisely explains the prolonged and pronounced estradiol level drop observed when taking ATD.
Authentic Boldenone: Classic anabolic
Authentic Boldenone (17β-hydroxyandrost-1,4-dien-3-one) is a testosterone derivative developed to increase muscle mass and strength. Its anabolic effects are realized through stimulation of protein synthesis in muscles after binding with androgen receptors.
Boldenone's interaction with aromatase is fundamentally different. It can undergo aromatization, i.e., convert to estrogens, but does so significantly weaker than testosterone. It's critically important to understand: Boldenone itself is not an aromatase inhibitor, especially not a powerful and irreversible one like ATD. Scientific literature contains no data confirming its ability to suppress aromatase activity and cause estradiol drop. Its structural features don't give it such properties.
Thus, sellers' claims that sharp estradiol drop is a "special property" of Boldenone are lies with no scientific basis. This effect unambiguously indicates ATD presence in the drug.
Table 1: Comparative biochemical properties of ATD and Boldenone
Metabolic trap: How ATD converts to Boldenone
As already mentioned, the key aspect of this fraud scheme is the metabolic connection between ATD and Boldenone.
Scientific studies convincingly prove that ATD serves as a precursor for Boldenone. The key study revealing this connection was conducted by Parr et al. in 2009. Scientists showed that after ATD administration, not only ATD itself is found in the body, but also Boldenone directly, along with its main metabolites. Biochemically, this process likely involves reduction of the keto group in the 17th position of the ATD molecule to a hydroxyl group, which converts it into a Boldenone molecule.
This fact creates perfect cover for dealers. If a user, faced with low estradiol symptoms, decides to do a doping test to check the drug, then the test for Boldenone or its metabolites will likely be positive. This misleads, strengthening false confidence that real, albeit "unusual," Boldenone is being used.
Pharmacokinetics of the counterfeit: Why this isn't a "long" ester
AAS users value Boldenone Undecylenate for its long-lasting action provided by the long ester chain. Its half-life is about 14 days. The ester slows the release of active substance from the oil depot into the blood.
In the case of counterfeit, the situation is completely different. ATD, being in oil solution, will gradually release and then metabolize into free (non-esterified) Boldenone. Non-esterified steroids have significantly shorter half-lives. Studies on horses show that the half-life of injectable non-esterified Boldenone is about 5.1 days (123 hours)—almost three times less than Undecylenate. In humans, this period would probably be even shorter.
This means that the anabolic effect from Boldenone formed from ATD will be unstable and short-term, which completely doesn't match expectations from a long-acting drug. The main noticeable and lasting effect will be estradiol suppression, since ATD's action on aromatase is irreversible and prolonged.
Economics of deception: Why counterfeiting is profitable?
The main driving force of this falsification is economic benefit. ATD synthesis is apparently a less complex and costly process. It can be obtained from relatively accessible and cheap precursors, for example, by oxidizing DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone)—a massively produced and available steroid.
Production of authentic Boldenone Undecylenate is a multi-stage process:
- Synthesis of Boldenone itself, for example, from testosterone
- Subsequent esterification (attachment of undecylenic acid ester), which requires additional reagents, equipment and complicates technology
Obviously, ATD's cost for underground labs is significantly lower than Boldenone Undecylenate. Selling cheap-to-produce ATD at the price of expensive and sought-after Boldenone provides fraudsters with maximum profit.
Health consequences and myth debunking
By buying counterfeit with ATD, the consumer exposes themselves to serious risks they're not informed about. Sharp and uncontrolled drop in estradiol levels, which plays an important role in the male body too, can lead to a whole range of negative consequences:
- Joint and muscle pain: This syndrome is well known and described in medicine as AIMSS (Aromatase Inhibitor-Associated Musculoskeletal Syndrome)
- Decreased libido and erectile dysfunction
- Mood deterioration, apathy, increased fatigue
- Long-term risks: With prolonged use, negative changes in lipid profile (cholesterol levels) and bone density reduction are possible
This isn't just substituting one substance for another, but replacing an anabolic agent with a drug having a completely different mechanism of action that carries its specific and dangerous side effects.
Conclusions for the user
Based on deep analysis of scientific data, the following key conclusions can be made:
- Different mechanisms of action: Authentic Boldenone is an anabolic that doesn't possess aromatase inhibitor properties. ATD is a powerful irreversible aromatase inhibitor causing estrogen level drops.
- Estradiol drop is a sign of counterfeit: If taking a drug labeled as "Boldenone" causes sharp estradiol reduction (confirmed by tests), you're most likely using a product containing ATD.
- ATD metabolizes to Boldenone: This fact is used by fraudsters to mask counterfeits. A positive Boldenone test doesn't guarantee product purity.
- Pharmacokinetic mismatch: Boldenone formed from ATD has a short half-life and cannot provide stable and lasting anabolic effect characteristic of Boldenone Undecylenate.
- Economic motive: Falsification is profitable for black market producers due to lower ATD cost.
- Health risks: Using such counterfeit exposes you to risks of developing side effects related to estrogen deficiency that sellers keep silent about.
I'm convinced that spreading reliable scientific information is a key tool for protection from deception. Understanding the real properties of these compounds will allow you to make informed decisions and avoid serious health harm. Therefore, if you want to clearly understand what you're using on cycle, preserve health and get positive effects rather than become a victim of fraudsters—contact me, Gregory Kandiba, for help. I'll help you figure everything out.
Scientific Sources:
- Parr, M. K., Fußhöller, G., Schlörer, N., Opfermann, G., Piper, T., Rodchenkov, G., & Schänzer, W. (2009). Metabolism of androsta-1,4,6-triene-3,17-dione and detection by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry in doping control. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 23(2), 207–218.
- Al-Snafi, A. E. (n.d.). Aromatase inhibitor-associated musculoskeletal syndrome: a scoping review of intervention studies. Journal of Pharmaceutical Negative Results, 13(Suppl 1), 300-310.
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2024). Aromatase Inhibitors. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
- ChEBI. (2021). androsta-1,4,6-triene-3,17-dione (CHEBI:131190). European Bioinformatics Institute.
- ChEBI. (2015). boldenone (CHEBI:34584). European Bioinformatics Institute.
- Macrides, F., Firl, A. C., Jr, Schneider, S. P., Bartke, A., & Steinberger, A. (1987). The aromatase inhibitor, 1,4,6-androstatriene-3,17-dione (ATD), blocks testosterone-induced olfactory behaviour in the hamster. Physiology & Behavior, 39(1), 141–145.
- Wallis, C. J., & Luttge, W. G. (1985). Two aromatase inhibitors inhibit the ability of a third to promote mating in male rats. Physiology & Behavior, 35(2), 189–193.
- PubChem. (n.d.). Boldenone. National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- Cohen, J., Collins, R., Darkes, J., & Gwartney, D. (2015). A league of their own: demographics, motivations, and patterns of use of 1,955 male adult non-medical anabolic steroid users in the United States. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 12(Suppl 1), P53.
- Schänzer, W. (2009). Differentiation between the administration of the aromatase inhibitor Androstatrienedione, and the anabolic androgenic steroids Boldione and Boldenone. World Anti-Doping Agency.
- Parr, M. K., Opfermann, G., Schänzer, W., et al. (2009). Metabolism of androsta-1,4,6-triene-3,17-dione and detection by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry in doping control. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 23(2), 207-218.
- Pozo, O. J., Van Eenoo, P., Deventer, K., & Delbeke, F. T. (2009). Detection and characterization of metabolites of boldione in human urine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 395(5), 1547–1559.
- Kwok, K. Y., Leung, G. N. W., Wan, T. S. M., Curl, P., & Schiff, P. J. (2015). Metabolic study of androsta-1,4,6-triene-3,17-dione in horses using liquid chromatography/high resolution mass spectrometry. *The Journokinetics of boldenone and stanozolol and the results of quantification of anabolic and androgenic steroids in race horses and nonrace horses. Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 30(2), 101-108.
- Razo-Jaramillo, J. J., Santes-Albarran, R., Chávez-Pacheco, J. L., De la Cruz-Aguilera, M. A., & Rubio-Osornio, M. (2024). Advanced trends in detecting boldenone, its metabolites, and precursors in biological matrices: an integrative review of chromatographic methods. Analytical Methods, 16(26), 3695-3711.
- WADA. (2018). Technical Document – TD2019IRMS. World Anti-Doping Agency.
- Schänzer, W. (2006). 13C/12C analysis of urinary boldenone and its main metabolite in trace amounts. World Anti-Doping Agency.
- Riemann, P., Müller, D., Gougoulidis, V., Flenker, U., Parr, M., & Schänzer, W. (n.d.). 13C/12C ratios of endogenous steroids after oral boldenone administration.
- Chan, G. H. M., Ho, E. N. M., Leung, D. K. K., Wong, K. S., & Wan, T. S. M. (2016). Targeted Metabolomics Approach to Detect the Misuse of Steroidal Aromatase Inhibitors in Equine Sports by Biomarkers Profiling. Analytical Chemistry, 88(1), 949–956.
Have questions or just want to discuss the article material?
Write to me anytime and I'll definitely try to help you!
For all types of communication:
